Home » Upper Limb Fracture Treatment
Welcome to Dr. Sayyad’s Orthopaedic Clinic – Your Trusted Destination for Orthopaedic Care
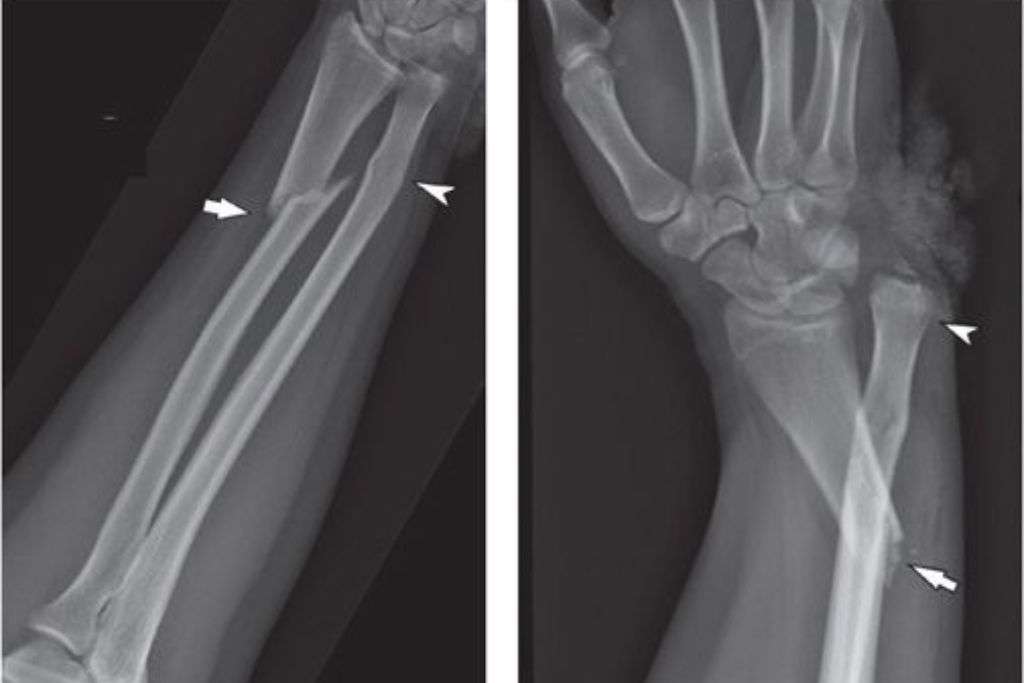
Upper limb fractures refer to breaks or fractures occurring in the bones of the arm, forearm, wrist, or hand. These injuries can result from various causes such as falls, accidents, or sports-related incidents. The primary symptoms of an upper limb fracture include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty in moving the affected limb. Prompt identification and appropriate treatment are crucial for optimal recovery.
Symptoms:
Pain: Severe pain is a common symptom of an upper limb fracture. The intensity may vary depending on the extent and location of the injury.
Swelling: The affected area often swells due to inflammation as the body’s natural response to the fracture. Swelling may contribute to increased pain and limited mobility.
Bruising: Bruising or discoloration may occur around the fracture site, indicating damage to blood vessels during the injury.
Deformity: In some cases, the fractured limb may appear deformed or out of its normal alignment. This can be visually noticeable and may require immediate medical attention.
Limited Range of Motion: Individuals with an upper limb fracture may experience difficulty moving the affected arm or hand. The range of motion may be restricted due to pain and swelling.
Treatment:
Medical Evaluation: A thorough examination, often including X-rays, is crucial for an accurate diagnosis of the type and severity of the fracture. This assessment guides the choice of treatment.
Immobilization: For less severe fractures, immobilization using splints, braces, or casts may be sufficient. This helps in keeping the broken bones in proper alignment and promotes healing.
Pain Management: Pain relief is a key aspect of treatment. Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications may be recommended to alleviate discomfort.
Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises are essential for restoring strength and flexibility after the initial healing phase. A physical therapist can design a customized program to aid in recovery.
Surgical Intervention: In cases of complex or displaced fractures, surgical intervention may be necessary. This could involve the use of screws, plates, or other fixation devices to stabilize the bones.
Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals are essential to monitor the progress of healing and adjust the treatment plan if necessary.
Complication Management: Complications such as infection or nerve damage require prompt attention. Monitoring for signs of complications is crucial during the recovery period.
Home Care: Patients are often provided with instructions on at-home care, including proper wound care, the use of supportive devices, and guidelines for gradually resuming daily activities.

