Welcome to Dr. Sayyad’s Orthopaedic Clinic – Your Trusted Destination for Orthopaedic Care
Hip impingement, also known as femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), is a condition where abnormal contact occurs between the hip bones, particularly the femur and the acetabulum. This impingement can lead to pain, restricted range of motion, and potential damage to the hip joint. Hip impingement treatment encompasses a comprehensive approach aimed at alleviating symptoms and preserving hip function.
Symptoms:
- Pain: Patients often experience pain in the groin area, which may radiate to the hip, lower back, or buttocks.
- Limited Range of Motion: Impingement can restrict the normal movement of the hip joint, leading to stiffness and reduced flexibility.
- Clicking or Catching Sensation: Some individuals may notice clicking or catching sensations during hip movements.
- Painful Activities: Pain may intensify during activities like walking, sitting for extended periods, or participating in sports.
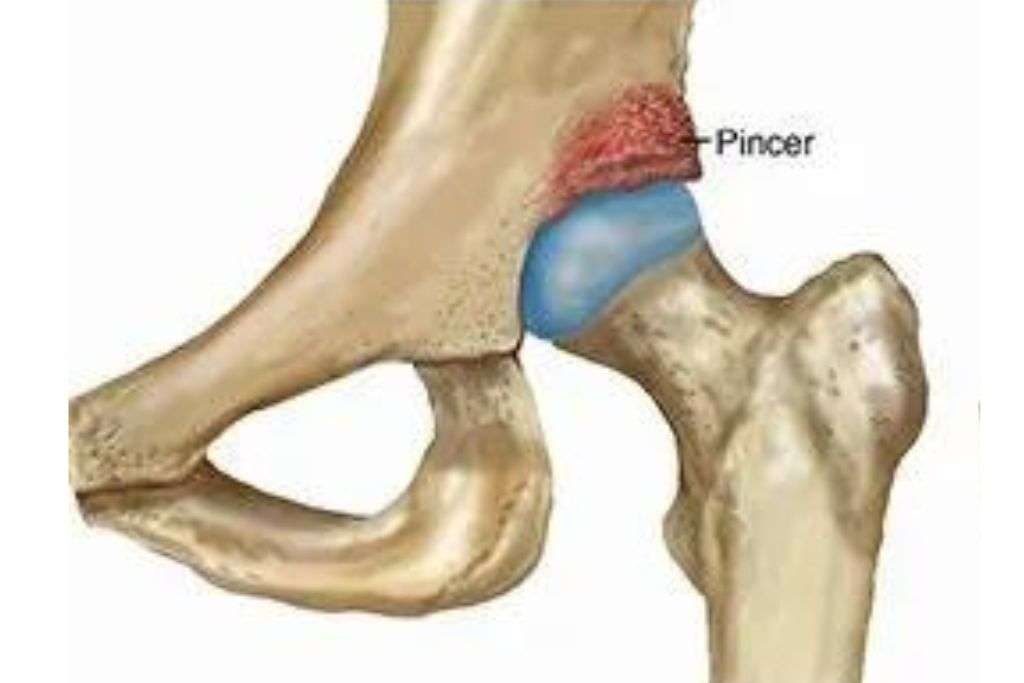
Types of Hip Impingement:
- Cam Impingement: Involves a misshapen femoral head, causing abnormal contact with the hip socket.
- Pincer Impingement: Results from excessive coverage of the femoral head by the acetabulum, leading to impingement.
Diagnosis:
Medical professionals use a combination of clinical assessments, imaging studies (X-rays, MRIs), and patient history to diagnose hip impingement.
Treatment Options:
Conservative Management:
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises help strengthen muscles around the hip, improving joint stability and reducing symptoms.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding certain movements or activities that exacerbate symptoms.
- Medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can alleviate pain and inflammation.
Intra-articular Injections:
- Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections may provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
Surgical Interventions:
- Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to address impingement by reshaping bone abnormalities and repairing damaged cartilage.
- Osteotomy: Surgical alteration of the hip bones to improve joint mechanics and alleviate impingement.
Rehabilitation:
- Post-surgery, rehabilitation involves a structured program to restore strength, flexibility, and functionality.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight management and avoiding activities that put excessive stress on the hip joint are crucial for long-term success.
Prognosis:
With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many individuals experience significant improvement in symptoms and a return to normal activities. However, the success of treatment depends on factors such as the severity of impingement, the chosen intervention, and adherence to rehabilitation.

