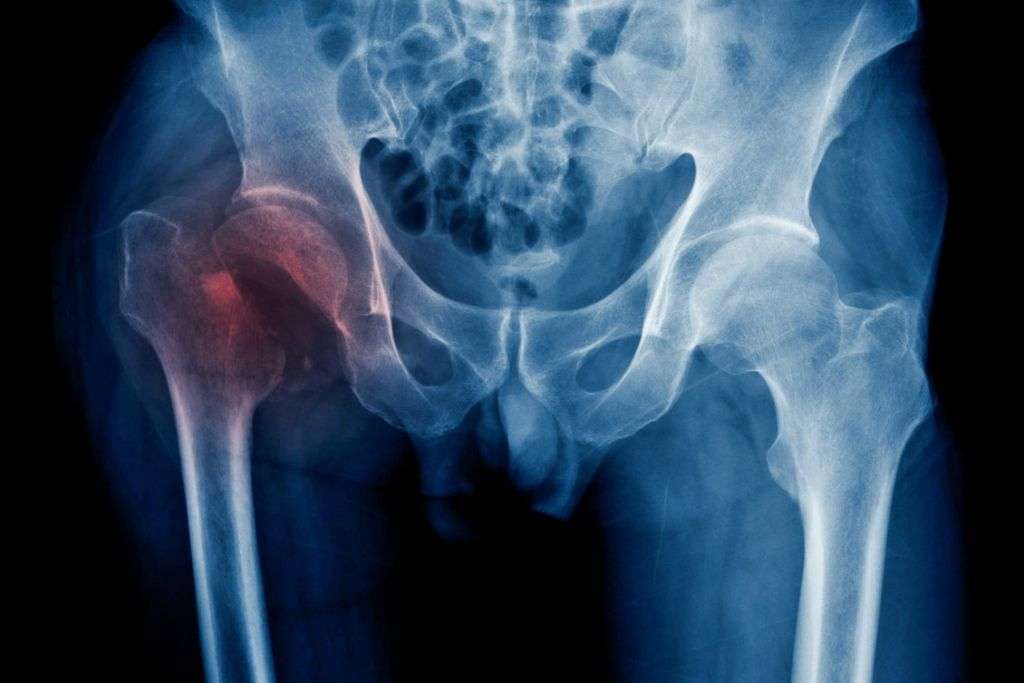
A hip fracture is a serious injury that involves a break in the upper part of the femur (thigh bone) or the pelvic bone around the hip joint. This injury is commonly associated with aging and osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones. Hip fractures often require prompt medical attention due to their impact on mobility and the potential for complications.
Causes:
Several factors contribute to the occurrence of hip fractures:
Osteoporosis: Weakening of bones due to aging or other medical conditions makes them more susceptible to fractures.
Trauma: A fall or direct blow to the hip, often seen in accidents or sports injuries, can cause fractures.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as cancer or metabolic disorders, can weaken bones and increase the risk of hip fractures.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of proper nutrition, particularly calcium and vitamin D, can contribute to bone fragility.
Medications: Long-term use of certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can weaken bones and increase fracture risk.
Symptoms:
Signs and symptoms of a hip fracture may include:
Severe Pain: Sudden and intense pain in the hip or groin area is a common symptom.
Inability to Bear Weight: Difficulty or inability to put weight on the affected leg.
Swelling and Bruising: Swelling and bruising around the hip or thigh area may be visible.
Leg Shortening or Rotation: The injured leg may appear shorter or turned outward compared to the unaffected leg.
Limited Range of Motion: Reduced ability to move the hip or perform certain movements.
Diagnosis:
A healthcare professional will perform a physical examination, assess the patient’s medical history, and order imaging studies, such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), to confirm the presence and severity of the hip fracture.
Treatment:
Treatment for a hip fracture often involves surgical intervention, especially for displaced fractures. Common surgical procedures include:
Hip Pinning or Fixation: Stabilizing the fracture using screws, pins, or plates.
Hip Replacement: In cases of severe fractures, a partial or total hip replacement may be necessary.
Rehabilitation: Following surgery, rehabilitation and physical therapy are crucial for restoring strength, flexibility, and mobility. This helps prevent complications such as blood clots and pneumonia.

