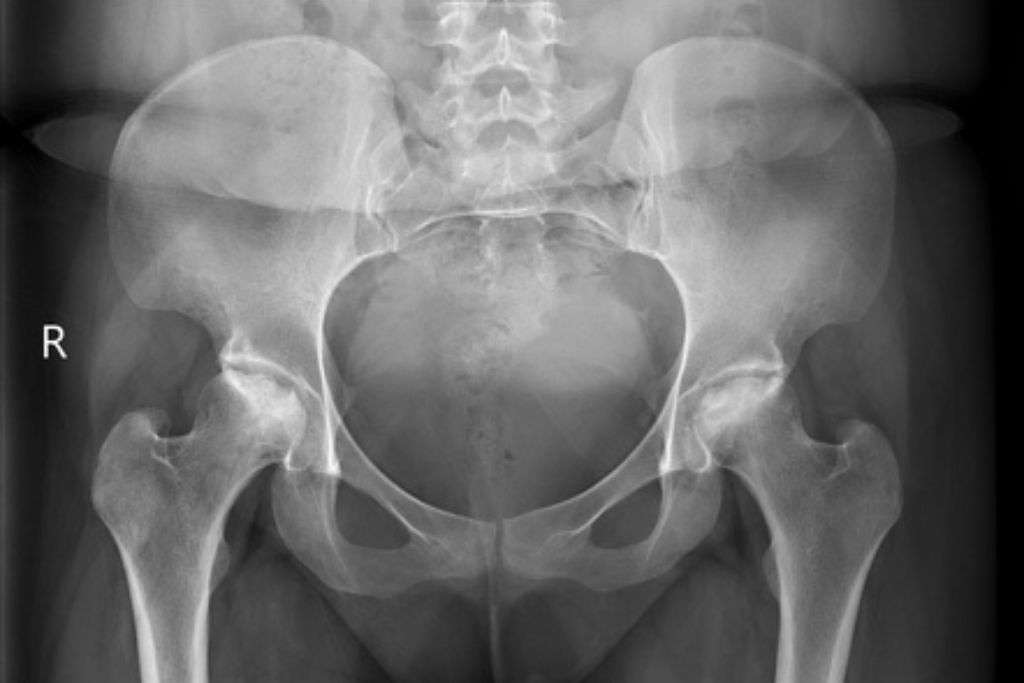
Avascular Necrosis (AVN) of the hip, also known as osteonecrosis or ischemic necrosis, is a condition characterized by the death of bone tissue in the hip joint. This occurs when the blood supply to the femoral head, which is the “ball” of the hip joint, is disrupted, leading to the gradual deterioration of the bone.
Causes:
- Trauma: Hip AVN can be triggered by a traumatic injury, such as a hip dislocation or fracture, which disrupts the blood vessels supplying the femoral head.
- Steroid Use: Prolonged or high-dose use of corticosteroid medications is a common cause, as steroids can interfere with blood flow to the bones.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is associated with a higher risk of AVN, as it may affect blood circulation and compromise the bone’s ability to regenerate.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, including sickle cell anemia, lupus, and HIV, can increase the risk of AVN.
- Joint Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus can contribute to AVN by affecting joint health and blood circulation.
Symptoms:
- Pain: Persistent pain in the hip joint, often on the affected side, is a primary symptom. The pain may range from mild discomfort to severe, limiting mobility.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the hip joint, especially after periods of rest, is common.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Individuals with hip AVN may experience a decreased range of motion in the affected hip, making activities like walking or climbing stairs challenging.
- Joint Instability: As the condition progresses, there may be a feeling of instability or weakness in the hip joint.
- Advanced Stage Symptoms: In advanced stages, the femoral head may collapse, leading to severe pain and immobility.
Diagnosis:
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and CT scans are commonly used to diagnose and assess the extent of AVN.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to identify underlying medical conditions or factors contributing to AVN.
Treatment:
- Conservative Measures: In the early stages, conservative approaches may include pain management, limiting weight-bearing activities, and physical therapy.
- Medications: Medications such as pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed.
- Core Decompression: This surgical procedure involves removing a portion of the inner layer of the bone to relieve pressure and stimulate blood flow.
- Bone Grafting: In more advanced cases, bone grafting may be performed to replace the damaged bone with healthy bone tissue.
- Joint Replacement: For severe cases where joint damage is extensive, total hip replacement surgery may be recommended.

